Robotic dexterous grasping is a fundamental operation in industrial automation and human-robot collaboration, yet the high-dimensional action space and diverse object shapes pose significant challenges for autonomous learning with multi-finger hands.
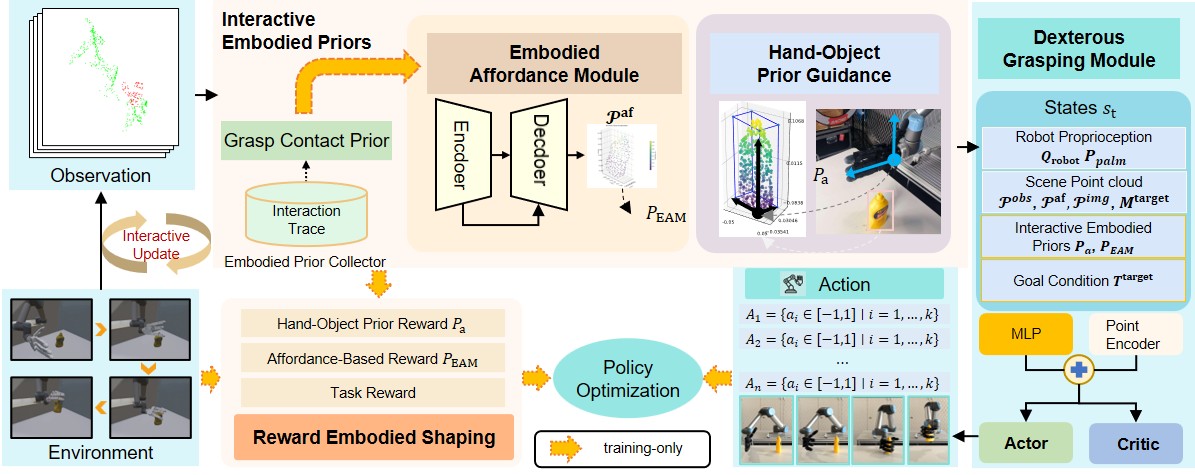
To tackle these issues, we propose IEP-Grasp, an autonomous grasping algorithm that integrates interactive embodied priors based on hand-object contact constraints into deep reinforcement learning with point cloud inputs, enabling the learning of both the final grasp pose and the dynamic grasping process. By focusing the agent's attention on critical grasping points, these priors enhance grasp stability and provide interpretable insights of hand-object interactions.
First, an unsupervised heuristic algorithm decomposes object point clouds into basic cuboid shapes, allowing a human-inspired hand-object prior guidance module to evaluate contact states and improve adaptability.
Our approach then refines a grasp affordance map through interactive exploration of contact patterns, enabling the agent to locate optimal hand-object configurations.
Finally, these interactive embodied priors are embedded into both observation and reward signals, synchronizing the learning of priors and the manipulation policy.
Extensive experiments in simulated and real-world environments with a 16-degree-of-freedom, four-fingered Allegro hand demonstrate significant improvements over baselines in grasp success rate and stability across diverse objects and categories.